mariPOC® CDI test
How to detect C.difficile infection?
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is the most commonly diagnosed cause of antibiotic and health care associated infectious diarrhoea. A typical patient diagnosed with CDI is an elderly person living in a long-term health care facility with recent history of antibiotic treatment for some other disease. C. difficile bacteria is an opportunistic pathogen which colonizes the intestine after antibiotic treatment has disturbed the normal microbiota. The CDI symptoms are caused by toxins A and B, produced by the bacterium, damaging the intestine cells.
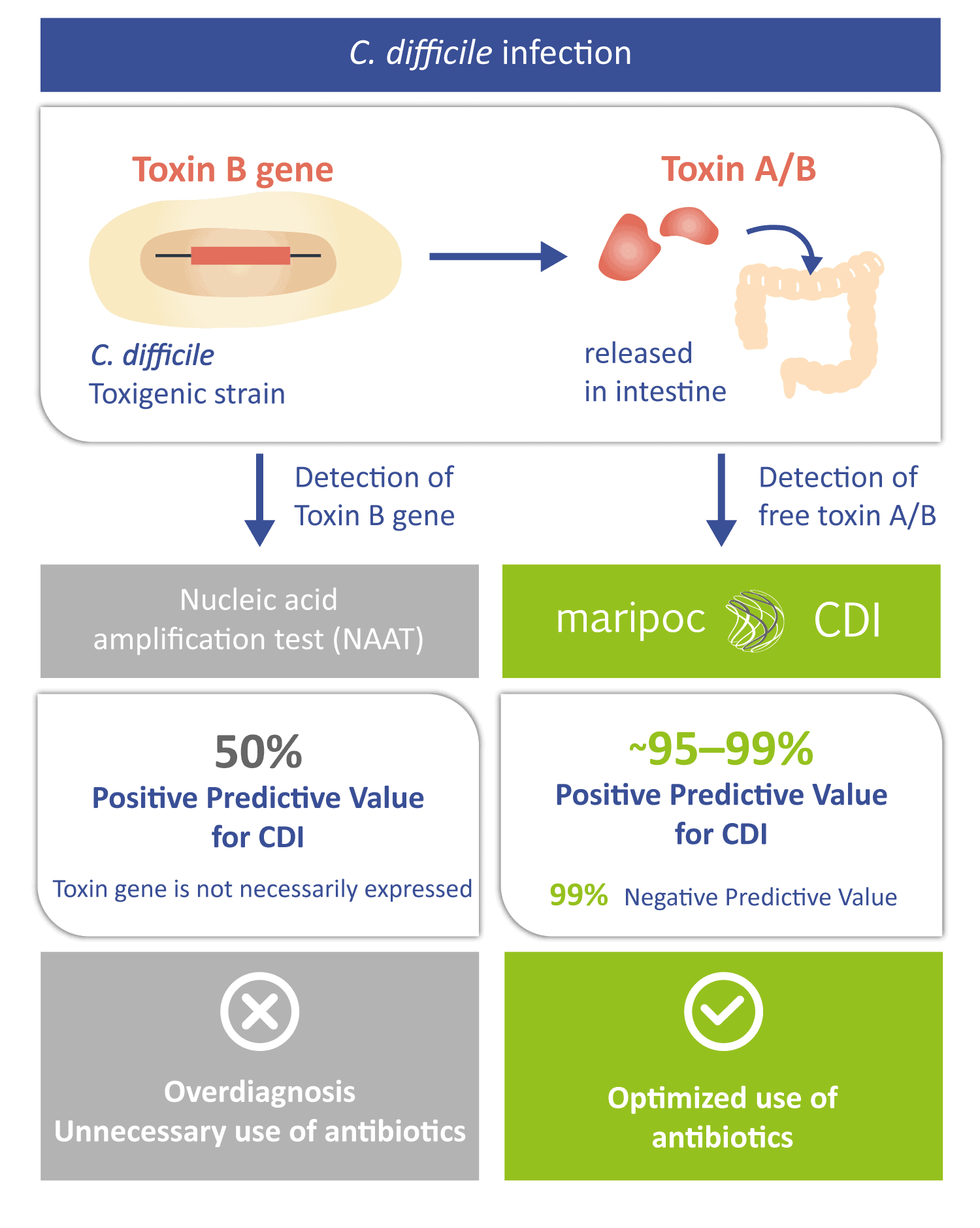
The disease-causing toxins A and B can be produced by only those C. difficile strains that have toxin gene i.e. toxigenic strains. Toxigenic C. difficile strain can be identified also by nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) methods. However, a positive toxin gene finding does not automatically mean that the infection is caused by C. difficile. The toxin gene is not necessarily expressed by the bacteria or it can be in harmless spore form. Therefore, free toxins might not be present in the intestine. Positive predictive value of the sole toxin gene detection can be as low as around 50% for CDI. Low positive predictive value leads to over diagnosis and prescription of unnecessary antibiotics. Therefore, the toxin A/B test with higher positive predictive value is needed to aid the diagnosis. The mariPOC® CDI test directly detects the disease-causing free toxins and therefore has a very high predictive value of almost 100%. Thus, the mariPOC® CDI test can be utilized for optimization of the use of antibiotics and to avoid unnecessary antibiotic treatments.
mariPOC® CDI test meets the latest ESCMID guidelines

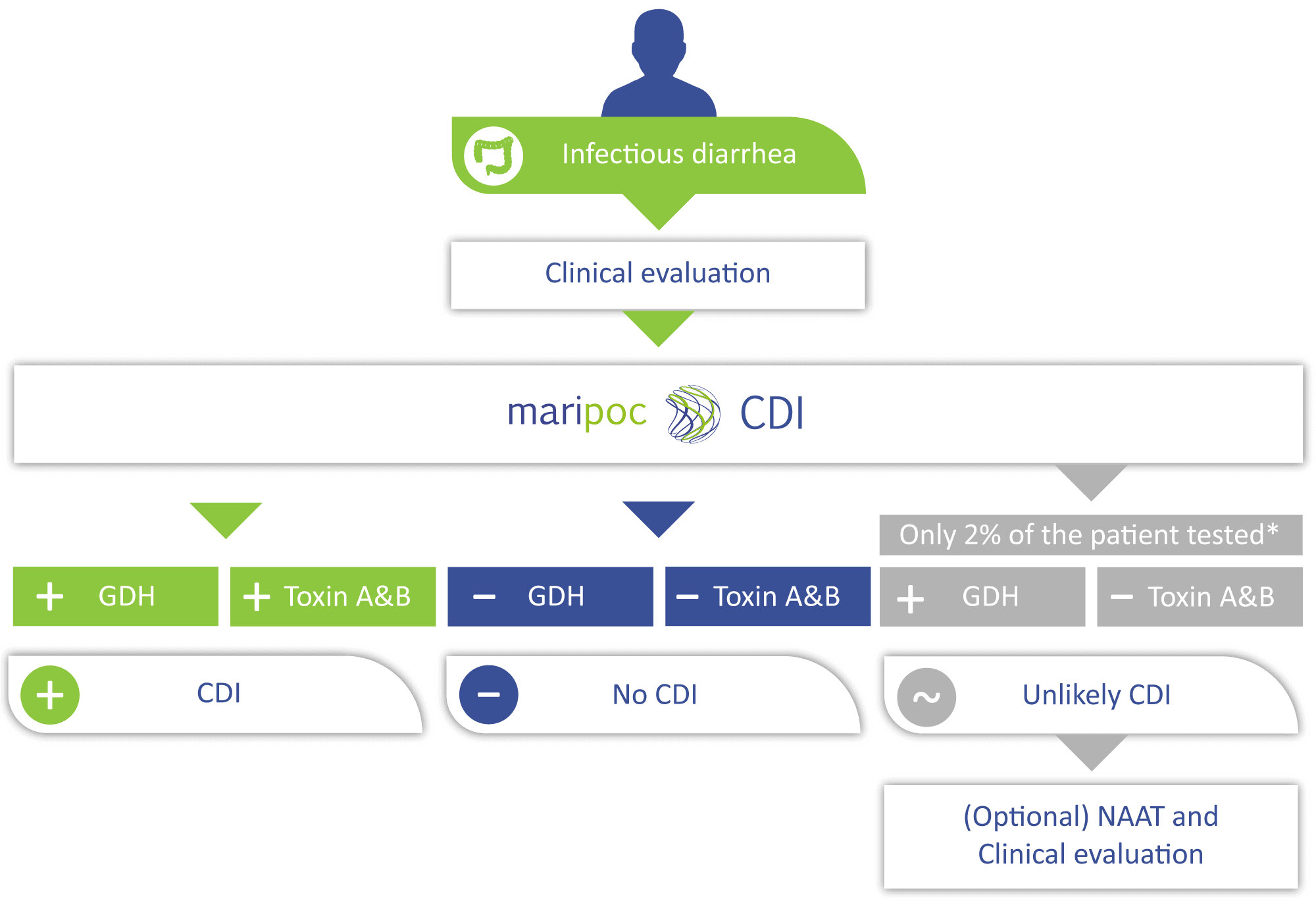
The mariPOC® CDI test was developed to meet the latest ESCMID (European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases) guideline for two-steps testing algorithm of CDI :
- Detection of C. difficile bacteria with highly sensitive test (GDH antigen detection test or toxin gene NAAT):
GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase) is a protein, produced by all C. difficile strains in large quantities. - Detection of disease-causing toxins A/B with antigen test having high predictive value:
Detection of free toxins A/B confirms C. difficile as the cause of the infection.
According to international guidelines, detection of the free C. difficile toxins from a faecal sample is an essential part of the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. mariPOC® CDI test detects C. difficile bacteria and free toxins A and B reliably and promptly.
The mariPOC® CDI test detects accurately and simultaneously C. difficile GDH and the disease-causing C. difficile toxins A and B from faecal specimens. The test provides the best accuracy in the market for rapid CDI diagnostics. Compared to the current market leader, mariPOC® test finds 20% more true toxin positive cases. This enables higher sensitivity than before in detecting CDI without the risk of over diagnosis.
mariPOC GDH test effectively excludes CDI with negative predictive value of 99.0%.
CDI test reports result from the same sample in two steps
20 minutes: Preliminary result (strong positive results)
2 hours: Final result (low positive and negative results)
mariPOC® Gastro and CDI
You can analyse mariPOC® Gastro and CDI tests simultaneously from the same specimen!
Hospitalized patients over the age of 65 are at risk for CDI. However, CDI cases are increasingly diagnosed for patients outside this risk group. The diagnosis may be delayed without suspicion of CDI or proper testing. Therefore, ESCMID recommends screening all unformed faecal samples for CDI. Furthermore, patients suspected to have CDI with toxin-negative specimen should get alternative diagnosis. The guideline aims to increase the detection of underlying cases of CDI and to find potential other causes of diarrhoea, respectively. In a recent study Krutova et al. (2019) evaluated the mariPOC® Gastro and CDI combi test with 640 faecal samples requested for CDI testing. mariPOC® Gastro CDI combi test was able to detect a ward epidemic caused by rotavirus. Furthermore, other infectious pathogen was found from 4.5% of the samples sent to the laboratory with clinical suspicion of CDI.
mariPOC® is the first automated and rapid multianalyte test to follow the latest diagnostic guideline for CDI and acute gastrointestinal infections cost-efficiently!